What is a pip in trading?
What are pips in leverage trading? Our article explains the basics of pips and ticks and how to use them when trading with OANDA
What are pips in leverage trading? Our article explains the basics of pips and ticks and how to use them when trading with OANDA
In this article you will learn:
- What a pip is and what it represents
- How to calculate gains and losses based on pips
- What is a pipette and why it was introduced
What does “pip” mean?
Pip stands for ‘percentage in point’. A pip in forex trading is the smallest standardized move by which a current quote can change. As it defines the change in price (for instance between two currencies), traders calculate the spread between the bid and ask prices of the traded instrument, and refer to the profit or loss that their position has made in terms of pips.
How does a pip work?
As mentioned above, each one pip move in your favor translates into a profit and every one pip move that goes against you translates into a loss. The size of that move determines how big the profit or loss is. Let’s focus on some real-life examples on how that translates to trading the markets.
How a pip works in currencies
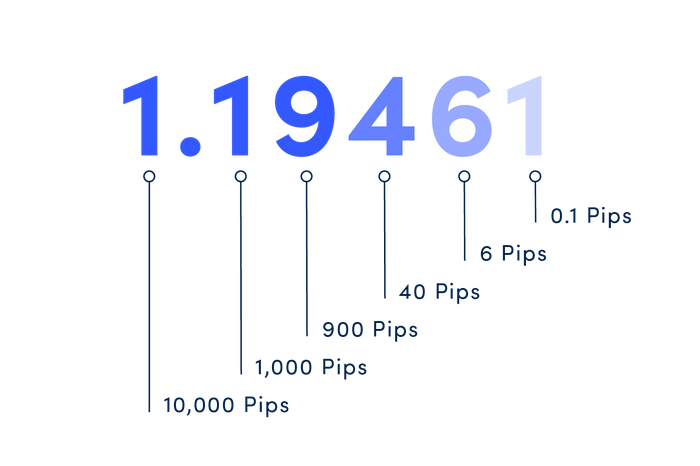
Most currency pairs are priced out to four decimal places and the pip change is the last (fourth) decimal point. One pip, therefore, is equivalent to 1/100 of 1% or one basis point.
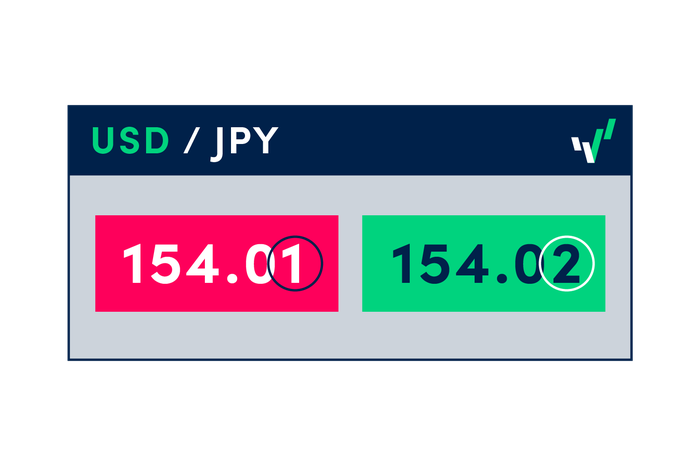
The Japanese yen is a notable exception, as these currency pairs are quoted to only two decimal places. To calculate a change in pips in forex trading for, say USD/JPY, you have to look at the second digit after the decimal point.
With a yen currency pair such as USD/JPY, a move of 154.01 to 154.02 would be a single-pip movement. This means that if you decided to enter a long position on the pair and closed your trade as price reached 154.51, you would make a 50-pip profit (154.51 - 154.01 = 0.50).
Let’s take a look at some examples. Let’s say you’re trading the EUR/USD currency pair. If the market were to move from 1.1600 to 1.1605, that 0.0005 increase would be a 5-pip move.
If you had entered a long position (clicking on buy), and the market moved from 1.1600 to 1.1650, and at that point you closed your trade, you would have made a profit of 50 pips (1.1600 - 1.1650 = 0.0050). Conversely, let’s say you had placed a stop loss at 1.1550 and the market moved against you, dropping from 1.1600 to 1.1550. Assuming there was no slippage, your stop-loss order would be hit and you would have made a loss of 50 pips (1.1600 - 1.1550 = 0.0050).
How pips work in other asset classes
The pip decimal position between instruments in other asset classes varies, just like it does for the Japanese yen. The reason for this is similar and depends on how many decimal places there are on the price of the instrument that is being quoted.
| Asset class | Instrument example | Pip placement |
| Currency | US dollar | 4 |
| Euro | 4 | |
| Japanese yen | 2 |
Gains and losses in pips
Example 1:
Let’s say you buy at 1.0598 to open a 100,000 unit trade on USD/CAD when it’s trading at 1.0597/1.0598.
When the value of USD/CAD rises to 1.0618/1.0619, you close the trade by selling at 1.0618. Given that one pip is a movement of 0.0001, you have made a profit of 20 pips (1.0618 – 1.0598 = 0.0020).
Example 2:
Let’s say you open an order to buy a 10,000 unit trade on USD/CAD when it’s trading at 1.0669/1.0670.
The value of USD/CAD falls to 1.0640/1.0641 and hits your stop loss, closing the trade for a 30-pip loss (1.0670 – 1.0640 = 0.0030).
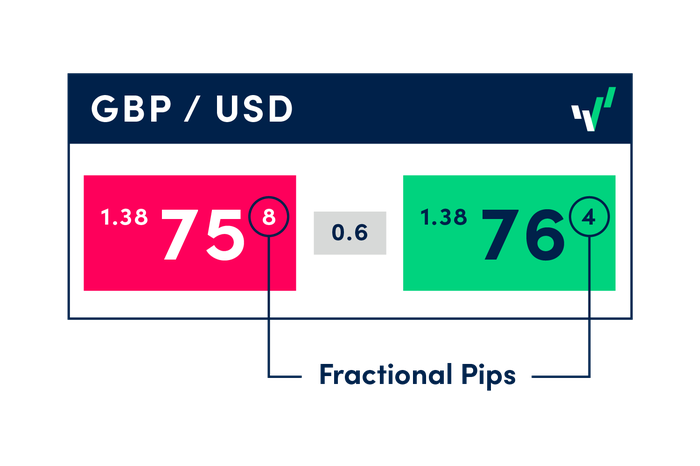
What is a pipette?
Fractional pips are known as "pipettes". A fractional pip is equivalent to 1/10 of a pip, giving you the EUR/USD currency pair with five decimal points, while yen pairs now extend to three decimal points. Pipettes are displayed in superscript format in the quote panel.
You can further build your knowledge of leverage trading by attending free live or recorded webinars that are conducted by our team of market analysts. Our webinars cover a range of strategies as well as how to use fundamental and technical analysis. Besides the introduction to leverage trading articles, you have access to live market analysis, premium webinars series and articles on basics of risk management.
This article and its contents are intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered trading advice.
Forex trading is high risk. Losses may exceed deposits.
Difference between leveraged and other forms of financial trading.
expand_less expand_moreUse fundamental analysis to your advantage.
expand_less expand_moreHow is technical analysis different from fundamental analysis?
expand_less expand_moreHow to build a robust trading strategy using indicators and oscillators.
expand_less expand_more